Contact:
Ministry of Health of the Slovak Republic
Role
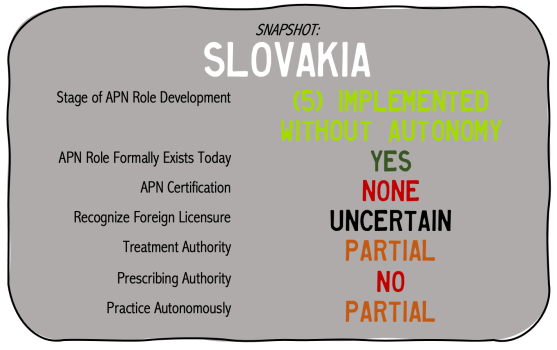
The role of the Advanced Practice Nurse (APN) was formally recognized in 2018 by the Ministry of Health in Slovakia (Grešš Halász, 2021). The role has been relatively recently introduced and evidence by Grešš Halász et al. (2021) demonstrated that APN’s have mixed perceptions about their own competence in practicing at a more advanced level, and practice confidence varied based on region within the country.
Healthcare in Slovakia historically was centralized by the government up until 1990. Afterward, the nation shifted to privatizing healthcare throughout the country, meanwhile mandating healthcare to remain not-for-profit. As much of advanced nursing practice is dependent on the abundance of trained nursing staff and the shortfall of more advanced medical professionals, the lower ratio of nurses per 1,000 people at 5.7 within the EU (compared to 8.4 of EU in general) likely contributes to the slower development of the APN role. Much of this gap is attributed to lower wages and lack of financial investment on behalf of the nation in healthcare staff, including education and health infrastructure (Slovak Spectator, 2021 Sep 14).
Education and Certification
Education for the APN in Slovakia is legislatively defined as “a nurse who graduated from at least the second university degree (equivalent to master’s degree) proceeded by the first university degree (equivalent to bachelor degree) in nursing, with specialization, and at least 5 years’ experience in a particular specialization, or a nurse without a specialization with 8 years of professional experience.” (Ministry of Health of the Slovak Republic, 2018).
Specialties
According to the Ministry of Health of the Slovak Republic (2018) there are several specializations recognized and identified within legislation. The additional roles expand on the level of independence the nurse may function. The basic nursing role is as follows.
- Nursing Practice (§ 95.1)
- Provide nursing diagnoses and follows treatment plans accordingly
- Perform assessment of the patient
- Provide ongoing nursing care/monitoring of patient
- Provide wound/ostomy care
- Provide patient education
Below are a list of the specializations with their added independent competencies:
- Nurse Specialist (§95.2)
- Can choose if a patient will have an intravenous cannula placed or not and can place that apparatus
- Follow dose range pharmaceutical operations.
- Nurse with Advanced Experience (§95.3)
- All care that of the Nurse Specialist (above)
- Provide advanced assessment
- Indicate and collect biological specimens (i.e. ordering lab analysis)
- Indicates treatment for nursing care
- Indicates treatment for preliminary wound care
- Nurse Midwife (§95.5)
- Provide traditional antenatal and postnatal care for mother and infant (up to 6 weeks post-natal)
- Performs childbirth, including if episiotomy if required
- Nurse Midwife Specialist (§95.6)
- All care that of a Nurse Midwife
- Can indicate and place intravenous cannula
- Nurse Midwife with Advanced Experience (§95.7)
- All care that of the Nurse Midwife and Nurse Midwife Specialist
- Advanced independence of indication of treatment
- Additional duties to manage nurse midwife care team
Have information to update this page?
References:
Grešš Halász, B. et al. (2021). Developing the advanced practice nursing role in Slovakia: Perception, education, and practice. Journal of the American Association of Nurse Practitioners. 33(11),916-923. doi: 10.1097/JXX.0000000000000460
Ministry of Health of the Slovak Republic. (2018) Decree determining the extent of nursing practice provided by a nurse independently, based on a medical doctor’s indication and in cooperation with a medical doctor and the extent of midwifery provided by a midwife alone, based on a medical doctor’s indication and in cooperation with a medical doctor. (no. 95/2018). The Ministry of Health Slovak Republic. http://www.epi.sk/zz/2018-95.
Slovak Spectator (2021, Sep 14). Hundreds of nurses have left their jobs in Slovak health care. Retrieved May 7, 2022 from: http://spectator.sme.sk